
|
Elizabethan II Study Group Journal: The Corgi Times Glossary |
P | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pair - two unsevered stamps, joined horizontally or vertically - the former being normally preferred by collectors. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pane - sheets of stamps are sometimes subdivided into sections by 'gutters'. Such divisions are known as 'panes' owing to their similarity to the panes of a window. A pane is usually a fourth or half of a sheet. A booklet pane is one complete leaf. |
 Pane |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Paper - the paper upon which stamps are printed. The quality normally used is a good machine-made white wove paper, with a surface suited to the printing process employed. Textured, or ribbed paper (as opposed to 'smooth' paper) can be found on some issues. Different paper manufacturers have supplied paper for Canadian stamps. In some cases, the gum can be used to differentiate the paper. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Par Avion - French for 'By Air'. |
Airmail label |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Part-perforate - a stamp imperforate on one or more sides, but with at least one side perforated. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Paste-Up - the area where the ends of rolls of coiled stamps are joined with glue or tape. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PCF - acronym for PostCard Factory postal cards. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
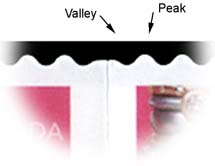
| Peak - the nickname given to the 'teeth' (or mountain) on a die-cut simulated perforation on a self-adhesive stamp. See Valley. |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Perfin - acronym for Perforated Initials. Stamps with punched holes in either a letter or design form indicating the company of usage. |
 Perfin |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Perforation - denotes, in philately, a series or row of round or other shaped holes, punched out between rows of stamps in a sheet (or coil) of stamps to facilitate partition, separation, or division. There are three basic methods of perforating employed today: (1) Line or guillotine, where one straight row of punches perforates a line at a time; (2) Comb, where three sides of each of a row are done at one stroke; and (3) Harrow, where a whole block, pane or sheet is perforate one operation, the punches being arranged in transverse rows. It is often difficult to detect the difference between 'comb' and 'harrow'. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Perforation gauge - perforations are measured by the number of holes (perfs)
found in 20mm, or 2
centimetres. - this figure is known as the perf number, and may be expressed in whole numbers of with a
decimal or fraction. Measurement is done by means of a gauge, which may be a simple printed scale on card or paper, or engraved on transparent plastic. Canada's self-adhesive stamps, separated by serpentine die cutting, are measured by the "peaks". |

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Permanent(tm) - the
non-denominated domestic postage rate for Canada
Post, introduced in November 2006.
|
 Permanent(tm) symbol |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Permit - a postage prepayment system whereby the licensee prints his registered 'permit' number on all postal package, hands the mail over the post office counter in bulk, and makes immediate cash payment. Is distinct and different from the 'metered mail' system. |
 Permit |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Peterborough -
a manufacturer of paper used on Elizabethan-era
stamps. First seen in February 1988. The gum is typically greyish and very shiny. |
 Inscription showing 'P' for Peterborough paper |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phantasy - a bogus stamp. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Philatelic - (phil-a-tel-ic) adjective of philately (phil-at-ely). Appertaining to the study of adhesive postage stamps. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Philately (phil-at-ely). (Greek Philo - lover, or fond of; ateleia - free of payment-or tax). The intelligent study of postage stamps and their production. A philatelist is is a student of philately. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Philometrist - collector of metered mail markings. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phosphor - 'invisible' ink (tagging) applied to the front of the stamp in vertical bars (one, two, or three have been used on Canadian stamps) or around all four sides of the stamp that, when exposed to ultraviolet light, activates a sorting and canceling machine.
Canada issued its first phosphor tagged stamps in 1962 in readiness for the installation of a British-made letter-facing machine in Winnipeg, Manitoba. |
 Phosphor tagging |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Photogravure - modern stamp-printing
process consisting of photographing the artist's
finished drawing on to process film and printing down on to sensitised carbon tissue which is transferred to a copper plate (or cylinder), and etched. Ink is forced into the design hollows, the surface wiped clean (see Doctor blade flaw), and picked up by the paper being pressed into contact with the
recessed design. See Lithography. |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pictorials - stamps with a 'picture' design - for example, landscapes, buildings, flowers, animals, etc. - as opposed to those of more traditional motif such as portrait or coat-of-arms. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Piece - see 'On piece'. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Plate (French cliché) - the base from which stamps are printed. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Plate numbers - the serial order of plate manufacture printed in the sheet margins. |
 Plate number block of 4 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Plate block - four or more stamps to which are attached the marginal paper bearing the printing plate or cylinder number inscription. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Plating - term used to describe the collecting of stamps according to their position on the sheet; in many issues, this can be determined by close study of the design. When stamps representing a complete sheet have thus been assembled, it is said to be a 'reconstructed sheet'. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| POCON - acronym for Post Office Computer Organization Number, introduced in 1973, replacing the MOON system. |
 POCON cancel |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Postage dues - or 'unpaid letter' stamps, are labels affixed to under-stamped postal packets at the office of delivery. It is the obligation of the postman to collect the amount indicated. The office of collection normally assesses the charge, weighs the packet, and indicates by handstamp the amount to be collected (double the deficiency). Where stamps are not used, the wrapper is often marked with the letter 'T' (French Taxe), the internationally accepted symbol. |
 Postage due |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Postal card - a government-produced postcard bearing an imprint in the upper right corner representing prepayment of postage. |
 Postal card |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Postal
code - Canada's postal code system is based on
a combination of letters and numbers in the format
ANA NAN (A=alpha, N=Number), based on geographical
coordinates. Example: R3C 1L5 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Postal history - (1) the study of postal markings, rates and routes; (2) anything to do with the history of the posts. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Postal stationery - various types of stationery including envelopes, letter-sheets (aerogrammes), letter-cards, postcards, and wrappers, usually but not necessarily of the kind sold at post offices, and officially imprinted with a non-adhesive stamp. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Postally used - implies that a stamp bears irrefutable evidence of having been genuinely and legitimately used to prepay postage. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Postcard - a small card, usually with a picture on one side and a space for a written message on the other. Postcards have no imprinted stamp. See Postal Card. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Postcard Factory -
prepaid postal cards,
first issued in 1997, depicting various Canadian
scenes on the front. The featured stamp is a
non-denominated version of the 45c Flag over
Building definitive. There are well over 500 different varieties ... and the list is still growing (as of June 2004). |
 Postcard Factory |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Postmark - any form of marking, with a postal meaning, applied to any kind of postal matter by a competent authority. The term is most often applied to the impression which gives the date of posting and the office of origin. Postmarks designed to cancel stamps so that they cannot be used again for postage are usually referred to as cancellations. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Post office seals - the adhesive labels used to re-seal damaged or opened postal packages. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precancels - machine-printed cancellations
applied by authority to save time in handling large blocks of mail, as stamps so treated normally do not require or receive further cancellation. The pre-cancellation usually consists of two (or three) groups of horizontal black double lines.
The numeral type of precancel has been in used in Canada since 1931. The numerals of the cities correspond with the accounting number assigned to the individual Post and Money Order office. In the Elizabethan-era, two stamps each had three different numerals:
In addition to black lines used on virtually all Canadian precancels, one stamp was released with red precancel lines. Precancel stamps were discontinued in 1980. |
 Precancels
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Printers - printers of Canadian Elizabethan-era stamps include: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Printer's waste - unfinished stamps removed from a high security printer's building by unscrupulous employees. Typically these will be imperforate or missing one (or more) colours or be 'test' samples of various colour combinations. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Printing - the four printing methods most commonly used for the production of postage stamps are: line-engraving (widely referred to as recess-printing); typography (letterpress); photogravure; and lithography. Some issues have been printed by more than one process, it is useful for the collector to learn to distinguish them.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Proofs - trial impressions, or 'progress' prints, classified as follows:
|
 Large Die Proof |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Provincial abbreviations - standardized two-letter abbreviations assigned to the Canadian provinces and territories (and the states in the USA). |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PVA - acronym for polyvinyl alcohol (or polyvinyl acetate). A form of
gum applied to the back of Canadian stamps. See self adhesive. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
© 2001-2017, 2018 Website design by: Adminware Corporation. For information or questions regarding this website, please contact Robin Harris |

